Authors: Jana S. Röder, Henning Boekhoff
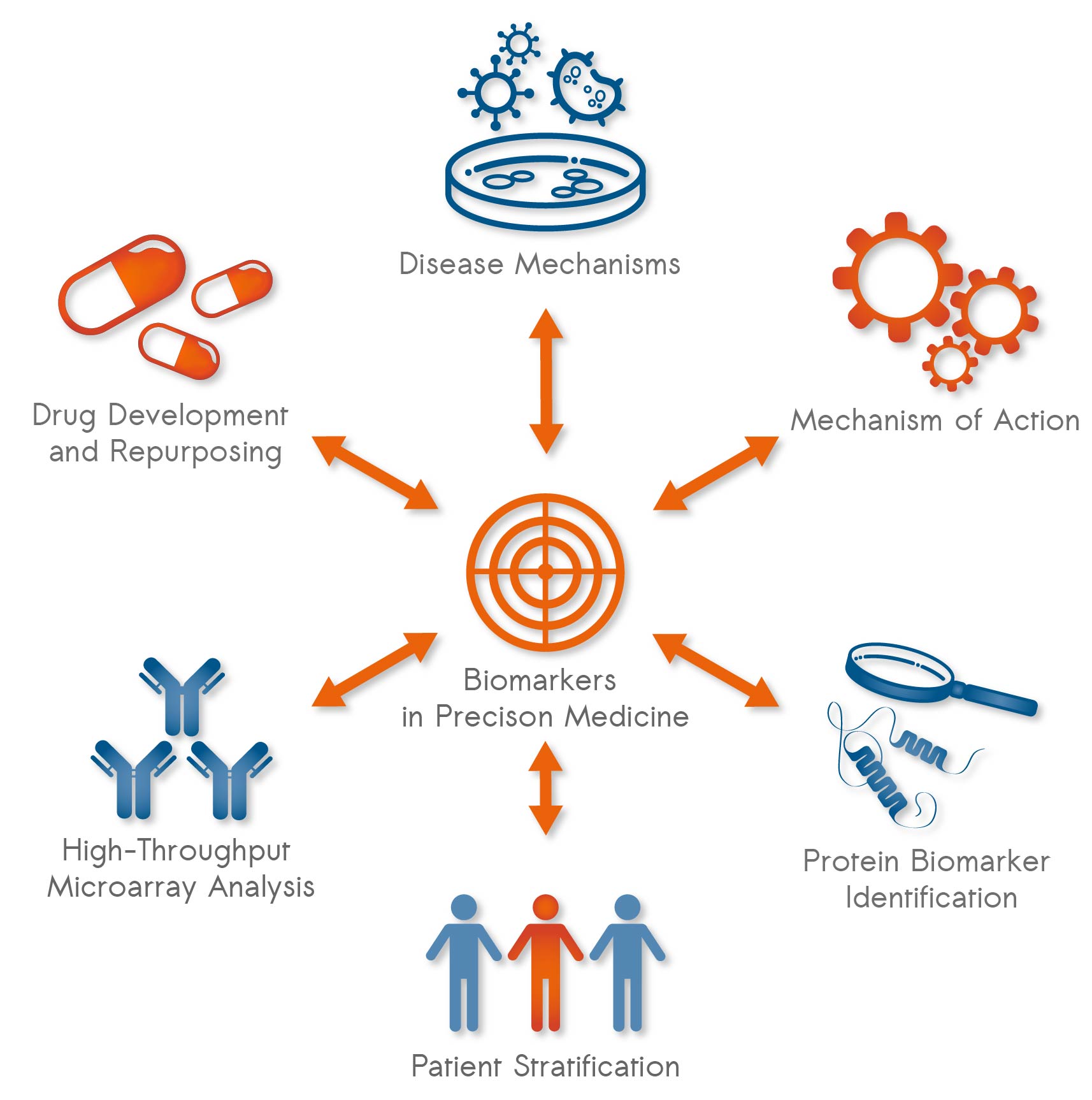
Biomarkers for Precision Medicine: Shaping Diagnostics and Medical Care
Modern medicine relies on precise diagnostics and reliable patient stratification to provide the best possible patient care. However, most diseases are still defined by symptom descriptions and selecting the best treatment option can be a trial-and-error approach. This places a burden on patients and healthcare systems, as treatments are often not as effective and as adapted to the disease as they should be. This can lead to undertreatment of certain patient subpopulations and even to adverse events without treatment benefit. Precision medicine aims to change this by using molecular mechanisms for disease definition and treatment selection.
Using molecular markers to define diseases would enable precise patient stratification and provide information about the underlying biological mechanisms. Once identified, mechanism-based treatments that target specific pathways would allow for a more tailored approach to patient care. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of both diseases and drugs could also lead to repurposing of existing drugs to provide previously unknown treatment options to new patient populations. Giving the right drug to the right patient at the right time requires novel biomarker signatures to efficiently stratify patients. At Sciomics, we specialize in biomarker discovery at the proteomic level to enable precision medicine. We have identified molecular biomarkers in a wide range of diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, organ failure, inflammatory diseases, and infections.
Efficient Profiling, Deep Insights: scioDiscover Biomarker Discovery
New protein biomarker signatures can be derived from various sample sources such as blood, urine, vesicles, cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated cells. The identification and validation of potential biomarker candidates can be accelerated by using high-throughput antibody microarray analysis, such as the scioDiscover platform for affinity-based proteomics. The scioDiscover biomarker discovery platform combines antibody-based profiling with high-throughput analysis and very low sample consumption. For instance, only 5 µL of plasma or serum is sufficient to obtain highly reproducible results. The abundance of more than 1,400 proteins is profiled in a single assay, covering key pathways of disease development, including cancer pathways, apoptosis pathways, the NFkB pathway, and many cytokines and their receptors. The antibody-based protein recognition reduces attrition rates and allows a rapid translation of results to other immune-based platforms - such as ELISA, CLIA, and LFDs - for further validation and diagnostic use.
Sciomics’ Biomarker Pipeline – from Discovery to Clinical Application
At Sciomics, we are using our scioDiscover platform to identify biomarker panels for the prediction of severe COVID-19 disease and for the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI).
We have discovered and systematically evaluated plasma protein biomarkers that can predict severe COVID-19 disease during the early phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection. After scioDiscover analysis, biomarker candidates were ranked and marker panels were selected using machine learning. Protein concentration measurements by ELISA were comparable to the results of the discovery study. Validated markers such as S100A8/A9 and CRP showed very good correlations between scioDiscover data and clinically available assays or ELISA, demonstrating the platform's seamless translation of results to other platforms. Early stratification of patients at high risk of developing severe or even critical disease could support treatment and care decisions, ultimately improving medical interventions and reducing the burden on healthcare systems. The scioDiscover workflow allows us to identify potential biomarker panels in a very short time. It took less than eight weeks from the start of wet-lab research on predictive COVID-19 biomarkers to patent filing.
In another project, we aim to develop a biomarker-based early diagnostic test for acute kidney injury (AKI). AKI is a sudden loss of kidney function that often occurs as a complication of other serious medical conditions. It leads to structural kidney damage, impaired filtration and potentially serious consequences, including the need for long-term dialysis and increased mortality. Early detection and intervention of AKI is critical for patients: It can reduce the extent of kidney damage and increase the chance of reversible AKI. In addition, the financial burden on healthcare systems due to prolonged intensive care unit (ICU) stays and dialysis treatments is significant. An accurate early diagnostic or even predictive test for AKI would allow early intervention and better treatment regimens, preventing long-term kidney damage, lifelong treatment and death. Our scioAKI project has identified promising early diagnostic biomarker combinations for perioperative AKI and will be extended to other patient groups. Our ultimate goal is to develop a reliable and cost-effective test for the early diagnosis of AKI in a clinical setting.

Precision Medicine in the Clinic: Molecular Markers Shaping Future Treatments
Medical specimens are a limited and valuable resource. It can take years or even decades to collect enough samples for a study. It is therefore critical to make the most of them by using the most efficient methods for data generation. A single antibody microarray-based discovery study provides novel putative biomarkers, insights into the underlying disease mechanisms, and information about the patient population, enabling in-depth cohort characterization. In this way, the scioDiscover accelerates research and knowledge generation, ultimately advancing precision medicine. The combination of a better understanding of disease mechanisms and of pharmacological mechanisms of action enables the development of new treatment regimens and personalized patient care. Matching more suitable treatments to new patient populations could be further accelerated through drug repurposing. It has enormous potential to streamline drug development by making already existing drugs available to additional patient populations that may respond to the treatment. For example, clinical trials of repurposed drugs could be simplified because toxicology and mode of action analyses have previously been performed. In addition, precise patient stratification using molecular markers can improve the success rate of clinical trials, reduce drug development costs, and ultimately ensure that the patients receive the right treatment at the right time. Scientists and regulators around the world are collaborating to make these approaches a reality, for example in the EU-funded project REPO4EU. We are pleased to have been part of this consortium from the beginning. Maximizing the efficiency of medical research by using comprehensive data is the way forward to precision medicine and more efficient healthcare.
Published: 18 January 2024