Authors: Henning Boekhoff, Jana S. Röder
 The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic posed significant challenges worldwide and raised critical questions in the scientific community. While some individuals experienced mild or asymptomatic infections, others faced a severe or critical disease progression with a high mortality rate, peaking in 30 % mortality of patients aged 85 or older. The need for rapid biomarker discovery for early prediction of COVID-19 progression became evident from the outset of the pandemic.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic posed significant challenges worldwide and raised critical questions in the scientific community. While some individuals experienced mild or asymptomatic infections, others faced a severe or critical disease progression with a high mortality rate, peaking in 30 % mortality of patients aged 85 or older. The need for rapid biomarker discovery for early prediction of COVID-19 progression became evident from the outset of the pandemic.
At Sciomics, we continuously develop and optimize specific antibody microarray platforms for in-house protein and post-translational modification profiling, establishing ourselves as a world leader in microarray-based biomarker discovery. In a recent study published in Nature Communications Medicine, we leveraged our expertise to identify early predictive biomarkers for COVID-19.
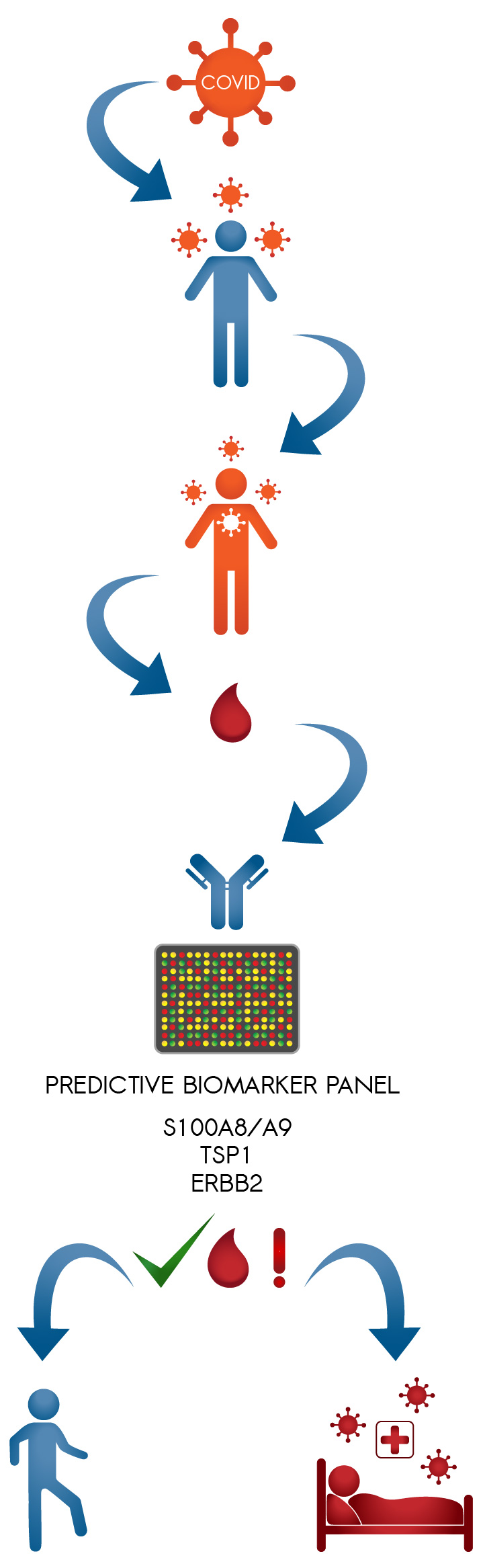
In the study, we analyzed 351 proteins in 53 human plasma samples at different infection stages. We identified proteins with varying abundances in patients with severe/critical and mild/moderate disease. Building on this, we analyzed 998 proteins in a larger cohort of 94 patients, leading to the selection of eleven promising biomarkers capable of predicting severe COVID-19.
We successfully established multiple biomarker panels, offering the potential to predict disease progression early and reliably stratify patients in clinical settings. The most promising biomarker panel identified consists of three proteins: S100A8/A9, TSP1, and ERBB2. We are actively working on validating these panels in COVID-19, Long Covid and other viral diseases of the respiratory system.
Early patient stratification for those at high risk of developing severe or critical disease could significantly improve treatment decisions, ultimately easing the burden on healthcare systems and leading to an improved pandemic preparedness. This biomarker signature showcases the use of biomarkers to predict disease progression and gain insights into disease mechanisms simultaneously.
Providing a bigger picture, unbiased or semi-targeted monitoring of the systemic response to a disease can shed light on diverse patient outcomes without prior knowledge of underlying mechanisms. Through antibody microarrays, thousands of proteins in various blood components can be examined simultaneously in a minimally invasive, low-volume, rapid, and less biased manner.
For more in-depth information on this biomarker discovery study for COVID-19, you can access the publication here.
Hufnagel, K., Fathi, A., Stroh, N., Klein, M., Skwirblies, F., Girgis, R., Dahlke, C., Hoheisel, J. D., Lowy, C., Schmidt, R., Griesbeck, A., Merle, U., Addo, M. M., & Schröder, C. 2023. Discovery and systematic assessment of early biomarkers that predict progression to severe COVID-19 disease. Communications medicine, 3(1), 51. DOI: 10.1038/s43856-023-00283-z
Published: 28 Nov 2023

